The Todd Mlsna Lab
Analytical and Environmental Chemistry
NSF Chemistry Department REU Program 2019
The NSF funded Research Experience for Undergraduates: Food, Energy, Water Security (NSF: REU-INFEWS) is in full swing! Eightstudents were selected for the REU-INFEWS program, with an additional 21 students participating in activities through external funding support. We are hosting students from 17 different colleges and universities. Our cohort of 42 students are all engaged in research activities for the summer along with social and career-building experiences to guide them toward future careers as scientists. MSU is proud to host such a large and talented group of students for our summer program.
The Mlsna Group Welcomes two Fulbrighters

June 2019
Beatrice Arwenyo and Jacinta Alchouron recently joined the Dr. Todd Mlsna group in the Department of Chemistry on Fulbright Scholarships. Beatrice came from Uganda on Fulbright Foreign Student grant to pursue her PhD in Chemistry. She joined the Todd Mlsna group in the fall of 2018. Her research focus is on the use of biochar for sustainable soil management. Jacinta came from Argentina on a Fulbright - Bunge & Born, short term research grant. This is her second summer in the Mlsna lab to work on the optimization of magnetized biochar synthesis using culms obtained from selected species of woody bamboos (Poaceae, Bambusoideae, Bambuseae) and its evaluation as remedial material for arsenic contaminated water.
They feel very fortunate to have had the opportunity to be part of the Department and the University because they have learned how to access the natural world with its beauty and complexities in a more realistic and practical way since their arrival. They are very grateful to the Fulbright organization for the life changing scholarships.
Beatrice Arwenyo and Jacinta Alchouron recently joined the Dr. Todd Mlsna group in the Department of Chemistry on Fulbright Scholarships. Beatrice came from Uganda on Fulbright Foreign Student grant to pursue her PhD in Chemistry. She joined the Todd Mlsna group in the fall of 2018. Her research focus is on the use of biochar for sustainable soil management. Jacinta came from Argentina on a Fulbright - Bunge & Born, short term research grant. This is her second summer in the Mlsna lab to work on the optimization of magnetized biochar synthesis using culms obtained from selected species of woody bamboos (Poaceae, Bambusoideae, Bambuseae) and its evaluation as remedial material for arsenic contaminated water.
They feel very fortunate to have had the opportunity to be part of the Department and the University because they have learned how to access the natural world with its beauty and complexities in a more realistic and practical way since their arrival. They are very grateful to the Fulbright organization for the life changing scholarships.
Cover of Applied Nano Materials
June 2019
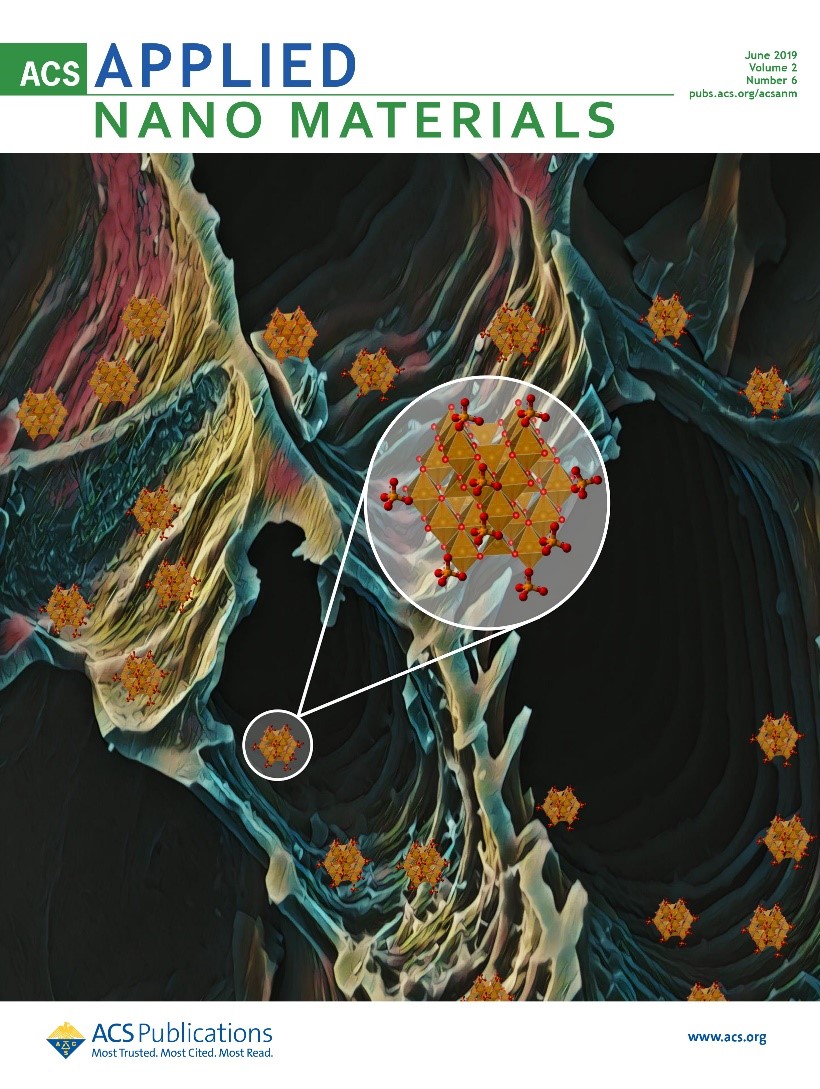
The recent work by Todd Mlsna group has been featured on the front cover of ACS Applied Nano Materials (June issue).
This graphic illustrates chemically coprecipitated magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles (~16.7 nm diameter) dispersed on a high-surface-area (~695 m2/g) syn gas by product Douglas fir biochar. The prepared composite material performed approximately 20 times better than bare magnetite nanoparticles for sorptive removal of phosphate. The possible chemisorbed phosphate surface species bidentate (corner and edge sharing) and monodentate are displayed on the enlarged section. This study effectively demonstrated a strategy to combat the limitations (surface area, particle aggregation, pressure drop in columns, nanotoxicity, and commercialization difficulties) of using nano-iron oxides in commercial sorption applications.
Link to the cover - https://pubs.acs.org/toc/aanmf6/2/6
Karunanayake, A. G., Navarathna, C., Gunatilake, S., Crowley, M., Anderson, R., Mohan, D., ... & Mlsna, T. E. (2019). Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Dispersed on Douglas Fir Biochar for Phosphate Sorption. ACS Applied Nano Materials. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.9b00430
The recent work by Todd Mlsna group has been featured on the front cover of ACS Applied Nano Materials (June issue).
This graphic illustrates chemically coprecipitated magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles (~16.7 nm diameter) dispersed on a high-surface-area (~695 m2/g) syn gas by product Douglas fir biochar. The prepared composite material performed approximately 20 times better than bare magnetite nanoparticles for sorptive removal of phosphate. The possible chemisorbed phosphate surface species bidentate (corner and edge sharing) and monodentate are displayed on the enlarged section. This study effectively demonstrated a strategy to combat the limitations (surface area, particle aggregation, pressure drop in columns, nanotoxicity, and commercialization difficulties) of using nano-iron oxides in commercial sorption applications.
Link to the cover - https://pubs.acs.org/toc/aanmf6/2/6
Karunanayake, A. G., Navarathna, C., Gunatilake, S., Crowley, M., Anderson, R., Mohan, D., ... & Mlsna, T. E. (2019). Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Dispersed on Douglas Fir Biochar for Phosphate Sorption. ACS Applied Nano Materials. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.9b00430
Todd and Deb Mlsna Lead Alternative Energy Study Abroad

May 2019
For 3 weeks in May of 2019, 28 students and 4 chaperones from MSU traveled to Europe to walk on black beaches and swim in hot springs near the Arctic Circle. They saw geysers, waterfalls, fjords and glaciers. They explored four of Europe’s most fascinating capital cities, Reykjavik, Oslo, Stockholm and Copenhagen with a curriculum focused on renewable energy including geothermal (Iceland), hydro-electric (Norway) and wind power (Denmark). Students learn how these countries produce almost all their electricity in ways that help combat problems with climate change, population growth and fossil fuel depletion.
For 3 weeks in May of 2019, 28 students and 4 chaperones from MSU traveled to Europe to walk on black beaches and swim in hot springs near the Arctic Circle. They saw geysers, waterfalls, fjords and glaciers. They explored four of Europe’s most fascinating capital cities, Reykjavik, Oslo, Stockholm and Copenhagen with a curriculum focused on renewable energy including geothermal (Iceland), hydro-electric (Norway) and wind power (Denmark). Students learn how these countries produce almost all their electricity in ways that help combat problems with climate change, population growth and fossil fuel depletion.
Chemical Reviews Article
March 2019
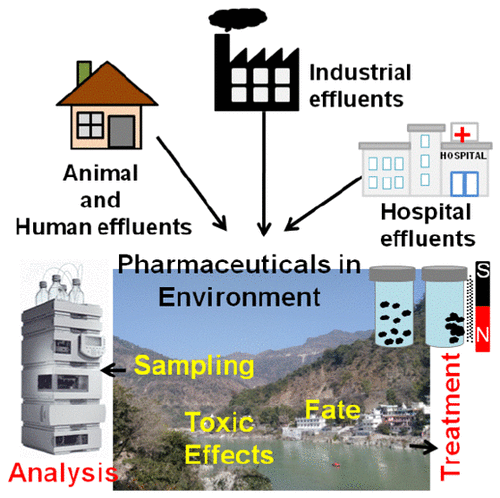
In the last few decades, pharmaceuticals, credited with saving millions of lives, have emerged as a new class of environmental contaminant. These compounds can have both chronic and acute harmful effects on natural flora and fauna. The presence of pharmaceutical contaminants in ground waters, surface waters (lakes, rivers, and streams), sea water, wastewater treatment plants (influents and effluents), soils, and sludges has been well documented. The Mohan, Pittman and Mlsna team has written a thorough review of methods used for their remediation from aqueous systems. This literature review (1990−2018) illustrates the rising environmental pharmaceutical contamination concerns as well as current analysis, remediation and management efforts.
Patel, Manvendra, Rahul Kumar, Kamal Kishor, Todd Mlsna, Charles U. Pittman Jr, and Dinesh Mohan. "Pharmaceuticals of emerging concern in aquatic systems: chemistry, occurrence, effects, and removal methods." Chemical reviews119, no. 6 (2019): 3510-3673. (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00299)
In the last few decades, pharmaceuticals, credited with saving millions of lives, have emerged as a new class of environmental contaminant. These compounds can have both chronic and acute harmful effects on natural flora and fauna. The presence of pharmaceutical contaminants in ground waters, surface waters (lakes, rivers, and streams), sea water, wastewater treatment plants (influents and effluents), soils, and sludges has been well documented. The Mohan, Pittman and Mlsna team has written a thorough review of methods used for their remediation from aqueous systems. This literature review (1990−2018) illustrates the rising environmental pharmaceutical contamination concerns as well as current analysis, remediation and management efforts.
Patel, Manvendra, Rahul Kumar, Kamal Kishor, Todd Mlsna, Charles U. Pittman Jr, and Dinesh Mohan. "Pharmaceuticals of emerging concern in aquatic systems: chemistry, occurrence, effects, and removal methods." Chemical reviews119, no. 6 (2019): 3510-3673. (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00299)